What are the Types of Company Class 12
Looking for what are the types (Kinds) of the company as per the syllabus of class 12 CBSE, ISC, and State Board
This topic is concerned with the Accounting for share capital chapter of accountancy class 12.
What are the kinds of company class 12
As the company act, 2013. Companies registered are classified as follows:
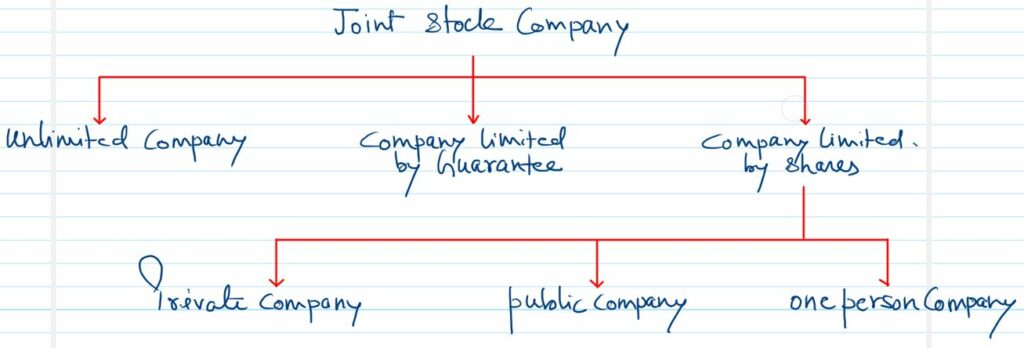
Unlimited Company:-
In this company the liability of its members is unlimited. If the company suffers a huge loss and the company’s assets are not enough to pay off debts. In such a case, members’ private assets are used to meet the claim of the creditors.
As the risk involved in such companies is too high, these are not found in India even though permitted by the companies Act.
Company Limited by Guarantee:-
In such a company, the liability of members is limited to the extent of guarantee given by them in the event of the winding-up of the company.
Company Limited by Shares:-
In the case of such a company, members’ liability is limited to share nominal value of shares purchased by them.
If a member has already the full amount of face value of shares purchased, he will not be liable to pay further.
If a member has partly paid shares, he can be forced to pay the remaining amount during the existence of the company as well as during the winding up.
Such companies are divided into
- Private company
- Public company
- one person company
What is Private Company Class 12
As per section 2(68) of the Companies Act, 2013, a private company is one which by its Articles of Association
- Restricts the right to transfer its shares
- limits the number of its members to 200.
- Prohibits any invitation to the public to subscribe for any securities i.e., shares or debentures of the company
The name of every private company must end with the words ‘Private Limited’.
What is Public Company class 12
As per section 2(71) of the Companies Act, 2013, a public company means a company that is not a private company.
following are the characteristics of a public company
- It can invite the public to subscribe to its shares.
- There is no restrictions on the transfer of its shares.
- A Public company must have at least 7 members
- A public company must have at least 3 directors but not more than 15 directors.
- The name of public company ends with the word ‘Limited’
This is only the public company that can raise its capital by issue of shares to the public for subscription.
What is One Person Company (OPC)
Section 2(62) of the Companies Act, 2013 defines One Person Company as ‘One Person Company means a company which has only one person as a member.
Rule 3 of the Companies (Incorporation) Rules, 2014 further prescribes that:
- Only a Natural Person who is an Indian Citizen and resident in India can be a member of OPC.
- One person can form only one OPC
- Its paid up share capital is not more than ₹50 lakh.
- Its average annual turnover of three years should not exceed ₹2 crore.
- As per Rule 3 (5) of the companies (incorporation) rules, 2014, an OPC can not be formed for charitable purposes, In othe words, it can be formed for business purpose only.
- An OPC can not convert itself into public or private company unless a period of 2 years has expired from the date of its incorporation and conversion is mandatory when paid up share capital exceeds ₹50 lakh or its average annual turnover during the relevan period exceeds ₹2 crore.


