Matching Type MCQs of Poverty chapter Indian Economic Development Class 12
Looking for important Matching type MCQs of Poverty chapter with answers of Indian Economic Development of Class 12 CBSE, ISC, UPSC and other state Boards.
We have compiled very important Multiple Choice Questions with answers of poverty chapter of Indian economic development of class 12
Multiple Choice Questions of Poverty chapter with answers of Indian Economic Development (Class 12)
Let’s Practice
Identify the correct sequence of alternatives given in Column II by matching them with respective terms in Column I
| Column – I | Column – II |
| a) Study Group formed by planning Commission for Poverty | (i) 2005 |
| b) ‘Task Force on Projections of the Minimum needs and Effective Consumption Demand’ | (ii) 1962 |
| c) Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act | (iii) 2014 |
| d) Jan Dhan Yojana | (iv) 1979 |
Choose the Correct Alternative:
a) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
b) (iii), (ii), (i), (iv)
c) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
d) (ii), (iv), (i), (iii)
Ans – d)
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct Alternative:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – National Sample Survey Organisation | i) Publish the data on poverty |
| B – MGNREGA | ii) Self Employment Programme |
| C – Fall in price of essential goods | iii) Reason of Poverty |
| D – Low capital formation means | iv) Low investment |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
D) D – (iv)
Ans – d)
Match the statements given under A with the correct options given under B.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (i) National Food for Work Programme | A. Self-Employment Programmes |
| B. Wage Employment Programmes |
Options
a) i – a
b) i – B
Ans – b)
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct alternative
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Niti Aayog | (i) Collects Data of poverty |
| B – National Statistical Office | (ii) Publish Data on Poverty |
| C – Head Count Ratio | (iii) Measures Poverty in Percentage |
| D – Economists identify poor | (iv) On the basis of calorie intake |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
D) D – (iv)
Ans – c)
Explanation:- Niti Ayog publish data, National Statistical Office collect data, Economists identify poor on the basis of occupationa and assets owned by them. Head count Ratio measures the poverty in percentage.
Match the statements given under A with the correct options given under B.
| Column – A | Column – B |
| (i) Relative Poverty | a) Refers to the total number of people living below the poverty line |
| (ii) Absolute Poverty | b) Refers to the poverty of people, in comparison to other people, regions, or nations. |
Options
a) (i) – a), (ii) – b
b) (i) – b), (ii) – a
Ans – b)
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct alternative:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Poor people | (i) Face stable employment |
| B – More poor are found in | (ii) Urban areas as compared to rural |
| C – As per the world Bank poor earn | (iii) Less than 1.9$ per capita per day |
| D – Poor do not face | (iv) Unemployment |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
d) D – (iv)
Ans – c)
Match the statements given under A with the correct options given under B.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (i) Transient Poor | a) They are never poor |
| (ii) Chronic Poor | b) They may be classified as churning poor and occasionally poor |
| c) It includes people who are always poor and those who are usually poor |
Options
a) i) – a), ii) – c)
b) i) – b), ii) – c)
c) i) – c), ii) – b)
d) i) – a), ii) – b)
Ans – b)
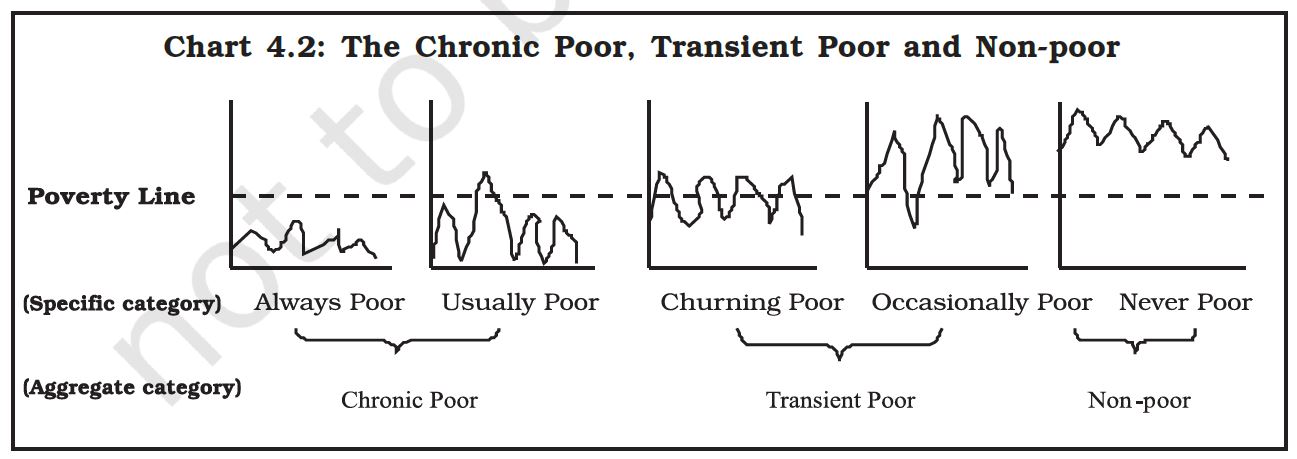
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct alternative:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Poverty line | (i) A separation line of absolute and relative poor |
| B – MPCE stands for | (ii) Monetary per Capital Expenditure |
| C – Occasionally poor are also known as | (iii) Non-Poor |
| D – Jan Dhan Yojana | (iv) Provide 5 lakh accidental insurance to bank holder |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
d) D – (iv)
Ans – c)
Explanation:- Poverty line separates poor and non poor, MPCE stands for monthly per capita expenditure, Jan dhan Yojana provides 1 lakh accidental insurance, occasionally poor are also known as non poor.
Identify the correct sequence of alternatives given in Column II by matching them with respective terms in Column I.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A) Mahatama Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act | i) 2014 |
| B) Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana | ii) 2005 |
| C) Launch of National Food for Work Programme | iii) 1989 |
| D) Formation of Expert groups to identify the number of poor in India | iv) 2004 |
Options
Choose the correct answer
a) A – (iii, B – (i, C – (iv, D – (ii
b) A – (iv, B – (i, C – (ii, D – (iii
c) A – (ii, B – (i), C – (iv, D – (iii
d) A – (ii, B – (iii, C – (iv, D – (i
Ans -c)
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct alternative:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Absolute poor | (i) When a comparison is done between two regions |
| B – Relative Poor | (ii) Person who is unable to get basic amenities |
| C – Antyodaya | (iii) A program to provide 100 days of guaranteed work |
| D – Poverty is multi-faceted | (iv) It has many dimensions |
Note:-
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
d) D – (iv)
Ans – d)
Explanation:- Absolute poor who is unable to get basic amenities, Relative poor when a comparison is made, Deendayal Antodaya Yojana is for skill development, Poverty has many dimensions
Identify the correct sequence of alternatives given in Column II by matching them with their respective years in Column I:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| a) Jan Dhan Yojana | i) 2005 |
| b) ‘Task Force on Projections of the Minimum Needs and Effective Consumption Deman’ | ii) 1962 |
| c) Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act | iii) 1979 |
| d) Study Group formed by Planning Commission for Poverty | iv) 2014 |
Choose the correct alternative from following:
a) (a) – (iv), (b) – (i), (c) – (ii), (d) – (iii)
b) (a) – (iv), (b) – (ii), (c) – (i), (d) – (iii)
c) (a) – (iv), (b) – (iii), (c) – (i), (d) – (ii)
d) (a) – (iv), (b) – (ii), (c) – (iii), (d) – (i)
Ans – c)
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct alternative:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Food for work | (i) It is noted program initiated in the 1990s |
| B – Rural Employment Generation Programme | (ii) It was launched in 1996 |
| C – National Urban Livelihood Mission | (iii) It replaced the Sampoorna Gramin Swarozgar Yojana |
| D – Pradhan Mantri Jana Dhan Yojana | (iv) It was launched in 2014 |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
C) C – (iii)
d) D – (iv)
Ans – d)
Explanation:- Food for work initiated in 2004, Rural Employment Generation Programme started in 1998, National Urban Livelihood Mission replaced Swarnajayanti Swarojgar Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana was launched in 2014.
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct alternative:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Absolute Poverty | (i) It involves the scarcity of luxury necessities. |
| B – Relative Poverty | (ii) rank the persons on the basis of relatively better off and worse. |
| C – Situational Poverty | (iii) It is a permanent type of poverty |
| D – Urban Poverty | (iv) It takes place in the rural area. |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
D) D – (iv)
Ans – b)
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct alternative:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Usually poor | (i) These are the people who sometimes have little more money but usually are unable to fulfill basic needs. |
| B – Churning Poor | (ii) These are the people who do not usually have sufficient money to fulfill their basic needs. |
| C – Occasionally poor | (iii) These people regularly move in and out of poverty |
| D – Always poor | (iv) These people reside in rural areas. |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
D) D – (iv)
Ans – a)
Explanation:- Churning poor, move in and out of poverty regularly, Occasionally poor simetimes get poor but mostly they are out of poverty, always poor resides in rural and urban both.
Identify the correct pair from Column I and Column II and choose the correct alternative:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Prime Minister’s RoZgar Yojana | (i) It was launched on 2nd October, 1893 |
| B – Swarna Jayanti Shahari Rozgar Yojana | (ii) It aims at creating self-employment and wage employment opportunities in urban areas. |
| C – National Rural Livelihood Mission | (iii) It was initially launched in 250 districts in 2012-13. |
| D – MGNREGA | (iv) It seeks to provide 200 days of guaranteed wage employment to at least one adult member of a household. |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
d) D – (iv)
Ans – b)
Explanation:- Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana was launched in 1993, NRLM was launched in June 2011, MGNREGA provides 100 days employment in a year guarantee.
Identify the correct sequence of alternatives given in Column II by matching them with respective terms in Column I
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Study group formed by Planning Commission for Poverty | (i) 2005 |
| B – Task-force on Projections of the Minimum Needs and Effective Consumption Demand | (ii) 1962 |
| C – Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act | (iii) 2014 |
| D – Jan Dhan Yojana | (iv) 1979 |
Options
a) A – (ii), B – (iii), C – (iv), D – (i)
b) A – (iii), B – (ii), C – (i), D – (iv)
c) A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iii), D – (iv)
d) A – (ii), B – (iv), C – (i), D – (iii)
Ans – d)
Select the correct combination between the following columns.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Chronic Poor | (i) Rich most of the time but may sometimes have a patch of bad luck. |
| B – Churning Poor | (ii) Who have never been poor. |
| C – Transient Poor | (iii) Always poor and usually poor who may sometimes have a little more money |
| D – Non – Poor | (iv) Regularly move in and out of poverty |
Options
a) A – (iv), B – (iii), C – (i), D – (ii)
b) A – (i), B – (iii), C – (iv), D – (ii)
c) A – (iii), B – (iv), C – (i), D – (ii)
d) A – (iv), B – (i), C – (iii), D – (iii)
Ans – c)
Choose the correct combination between the following columns:
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Insufficient income to provide for the minimum standard of living | (i) Relative Poverty |
| B – Poverty on the basis of comparison between nations and societies | (ii) Absolute Poverty |
| C – MGNREGA can into force | (iii) 2000 |
| D – Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yozana | (iv) 2006 |
Options
a) A – (ii), B – (i), C – (iv), D – (iii)
b) A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iv), D – (iii)
c) A – (ii), B – (i), C – (iii), D – (iv)
d) A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iii), D – (iv)
Ans – a)
Choose the correct combination between the following columns
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A – Prime Minister’s Rozgar Yojana (PMRY) | (i) One can get financial assistance in the form of bank loans to set up small industries |
| B – Swarna Jayanti Shahari Rozgar Yozana (SJSRY) | (ii) Educated unemployed from low-income families in rural and urban areas can get financial help to set up any kind of enterprise that generates employment |
| C – Rural Employment Guarantee Programme (REGP) | (iii) Creating employment opportunities both self-employment and wage employment in urban areas. |
| D – Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) | (iv) Provide guaranteed wage employment to every rural household whose adult volunteer is to do unskilled manual work for a minimum of 100 days in a year. |
Options
a) A – (iii), B – (iv), C – (i), D – (ii)
b) A – (ii), B – (iii), C – (i), D – (iv)
c) A – (iv), B – (ii), C – (iii), D – (i)
d) A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iii), D – (iv)
Ans – b)
Which of the following pair is incorrectly matched?
| Column – A | Column – B |
| A – Poverty line | (i) Line of demarcation between urban and rural people. |
| B – Poverty | (ii) Unable to satisfy conspicuous consumption but can meet basic necessities of life |
| C – Debt Trap | (iii) Usually arises due to higher interest rates or changes in terms and conditions of the debt incurred. |
| D – Moneylenders | (iv) Usually charges a very high rate of interest |
Options
a) A – (i)
b) B – (ii)
c) C – (iii)
D) D – (iv)
Ans – a)


