
50 Important Numerical of Value Added Method (National Income) with solutions class 12 CBSE Board
Hey, Welcome to Commerce School. Here we are going to solve 50 important Numerical of value added method of National Income with solutions. these numerical are very very important with point of view of the CBSE Board Examination.
Formula of Value Added Method of National Income
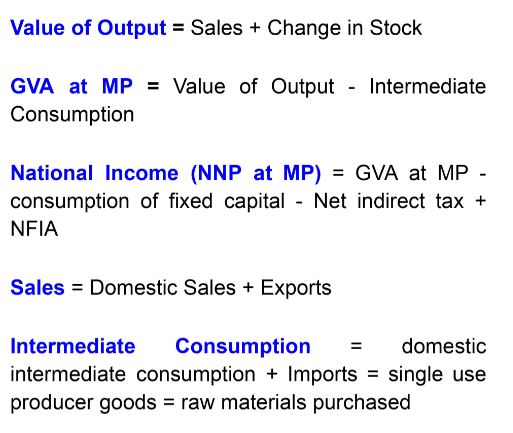
Other Formulas of Sales
- Sales = Sales to households + Sales to other firms + Exports
- Sales = Sales to households + Production for self consumption + Sales to other firms + Exports
| Download Value Added Method Formula | Download |
For more detail understanding you can read below guide on Value added Method
Read Here:- Value added method formula, tricks, notes, pdf
Must do Numerical of Value Added Method of National Income with solutions (explanations).
1. On the basis of the following data about an economy which consists of only two firms, find out:
a) Value Added by firm A and B, and
b) Gross Value Added or Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost.
Items
| Items | ₹ in lakhs |
| i) Sales by firm A | 100 |
| ii) Purchases from firm B by Firm A | 40 |
| iii) Purchases from firm A by Firm B | 60 |
| iv) Sales by firm B | 200 |
| v) Closing Stock of Firm A | 20 |
| vi) Closing Stock of Firm B | 35 |
| vii) Opening Stock of Firm A | 25 |
| viii) Opening Stock of Firm B | 45 |
| xi) Indirect taxes paid by both firms | 30 |
Answer:-
a)
Value of output of firm A = Sales of Firm A + Change in Stock (Closing Stock – Opening Stock)
Value of output of Firm A = i) + (v – vii)
Value of Output of Firm A = ₹100 + (₹20 – ₹25) = ₹ 95
Value Added by Firm A = Value of output of firm A – Intermediate Consumption of Firm A (Purchases of Firm A from other Firm)
Value Added by Firm A = ₹95 – ₹40 = ₹55 lakh
Value of output of Firm B = Sales of Firm B + Change in Stock (Closing Stock – Opening Stock)
Value of Output of Firm B = iv) + (vi – viii)
Value of Output of Firm B = ₹200 + (₹35 – ₹45) = ₹190
Value Added by Firm B = Value of output of Firm B + Intermediate Consumption of Firm B (Purchases of Firm B from other Firm)
Value Added by Firm B = ₹190 – ₹60 = ₹ 130 lakh
Read this lecture:- What is Intermediate Consumption ultimate Concept Clarity
b)
Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost (Gross Value Added at FC) = Value Added by Firm A + Value Added by Firm B – Indirect taxes paid by both firms
Gross Domestic Product at FC = ₹55 lakh + ₹130 lakh – ₹30 lakh = ₹155 lakh
Note- 1) Purchase of a firm from another firm is considered as intermediate consumption. 2) Value added by firms A and B implies gross value added at market price.
2. Calculate:–
a) Gross Value Added at Market Price, and
b) National Income from the following data.
| Items | ₹ in lakh |
| (i) Value of Output: a) Primary Sector b) Secondary Sector c) Tertiary Sector | 800 200 300 |
| (ii) Value of Intermediate inputs purchased by: d) Primary Sector e) Secondary Sector f) Tertiary Sector | 400 100 50 |
| (iii) Indirect taxes paid by all sectors | 50 |
| (iv) Consumption of fixed capital of all sectors | 80 |
| (v) Factor income received by the residents from rest of the world | 10 |
| (vi) Factor income paid to non-residents | 20 |
| (vii) Subsidies received by all sectors | 20 |
Solution:-
a)
Gross Value added at Market Price = Value of Output of all sector – Intermediate consumption of all sector
GVA at MP = a) + b) + c) – (d + e + f)
GVA at MP = ₹800 +₹200 +₹300 – (₹400 + ₹100 + ₹50) = ₹750 lakh
b)
National Income = GVA at MP – Consumption of Fixed Capital – Net Indirect Tax (Indirect Tax – Subsidy) + NFIA (Factor income from abroad – Factor income to abroad)
National Income = ₹750 lakh – ₹80 lakh – (₹50 – ₹20) + (₹10 – ₹20)
National Income = ₹630 lakh
Note:- There are 8 aggregates of National Income. In order to derive different figures, consumption of fixed capital, net indirect tax, and NFIA is adjusted
Watch my lecture over National Income and its related aggregates.
Subscribe to my YouTube Channel for Free Content
3. Find Gross Value Added at Market Price:-
| Items | (₹ in lakh) |
| i) Depreciation | 20 |
| ii) Domestic Sales | 200 |
| iii) Net Change in Stocks | (-) 10 |
| iv) Exports | 10 |
| v) Single use producer goods | 120 |
Solutions:-
Sales = Domestic Sales + Exports
Sales – ii) + iv) = ₹200 + ₹10 = ₹210
Change in stock = Net Change in Stocks = (-) 10
Intermediate Consumption = ₹ 120
Gross Value Added at MP = Sales + Change in stock – Intermediate Consumption
GVA at MP = ₹210 + ( – ₹10) – ₹120 = ₹80
Note: Single use producer goods are intermediate consumption
CBSE Delhi – 2016
4. Find Net Value Added at Market Price:
| Items | (₹ in lakh) |
| i) Fixed capital good with a life span of 5 years | 15 |
| ii) Raw Materials | 6 |
| iii) Sales | 25 |
| iv) Net Change in Stock | (-) 2 |
| v) Taxes on production | 1 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + Change in Stock
Value of Output = iii) + iv) = 25 + ( – 2) = 23
Gross Value Added at MP = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
GVA at MP = ₹ 23 – ₹ 6 = ₹ 17
Net Value Added at MP = GVA at MP – Consumption of fixed Capital
Consumption of Fixed Capital = Total value of fixed Capital/life span = 15/5 = ₹ 3 lakh
NVA at MP = ₹ 17 – ₹ 3 = ₹ 14
[CBSE Delhi – 2016]
Further Resources:-
Read Here:- 50+ Numerical of Income Method of National Income (Must Do)
Read Here:- 50+ Numerical of Expenditure Method of National Income (Must Do)
5. Find Net Value Added at Factor Cost:-
| Items | (₹ in lakh) |
| i) Durable use producer goods with a life span of 10 years | 10 |
| ii) Single use producer goods | 5 |
| iii) Sales | 20 |
| iv) Unsold output produced during the year | 2 |
| v) Taxes on production | 1 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + Change in Stock
Value of Output = iii) + iv) = ₹ 20 + ₹ 2 = ₹ 22
GVA at MP = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
Intermediate Consumption = Single use producer goods = ₹ 5
GVA at MP = ₹ 22 – ₹ 5 = ₹ 17
Consumption of fixed capital = Total value of durable use goods/Total life span = ₹10/₹10 = ₹ 1 lakh
Net Indirect tax = Taxes on production – subsidy of production = ₹ 1 – ₹ 0 = ₹ 1
Net Value added at FC = GVA at MP – consumption of fixed capital – Net Indirect tax (Indirect Tax – Subsidy)
NVA at FC = ₹ 17 – ₹ 1 – ₹ 1 = ₹ 15
[CBSE Delhi – 2016]
6. Calculate the Net Value Added at Factor Cost:
| S.N | Items | (₹ in lakh) |
| i) | Goods and Service tax | 25 |
| ii) | Consumption of fixed Capital | 5 |
| iii) | Closing Stock | 10 |
| iv) | Corporate tax | 15 |
| v) | Opening stock | 20 |
| vi) | Sales | 540 |
| vii) | Purchase of raw materials | 140 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + Change in stock
Value of Output = vi + ( iii + v) = ₹ 540 + ( ₹ 10 – ₹ 20 ) = ₹ 530
Gross Value added at Market Price (GVA at MP) = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
GVA at MP = ₹ 530 – ₹ 140 = ₹ 390
Net value added at factor cost (NVA at FC) = GVA at MP – Depreciation – Net Indirect tax (Indirect tax – subsidy)
NVA at FC = ₹ 390 – 5 – (25 – 0) = ₹ 360 lakh
Note:-
1) Goods and Service tax is the indirect tax
2) Corporate tax paid by the company to government and considered as a direct tax and thus is not considered here.
3) Purchase of raw materials is a intermediate consumption.
7. Calculate the Gross Value Added at Market Price
| S.N | Items | (₹ in lakh) |
| i) | Goods and service tax | 40 |
| ii) | Consumption of fixed capital | 15 |
| iii) | Closing stock | 20 |
| iv) | Sales | 700 |
| v) | Subsidy | 5 |
| vi) | Intermediate consumption | 400 |
| vii) | Opening Stock | 10 |
Solution
Value of Output = Sales + Change in Stock
Value of Output = iv + ( iii – vii) = 700 + ( 20 – 10 ) = ₹ 710
Gross Value Added at Market Price (GVA at MP) = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
GVA at MP = ₹ 710 – ₹ 400 = ₹ 310 lakh
8. Calculate gross value added at market price.
| S.N | Items | (₹ lakh) |
| i) | Goods and service tax | 30 |
| ii) | Sales | 800 |
| iii) | Depreciation | 50 |
| iv) | Net Change in stocks | – 40 |
| v) | Purchase of raw materials | 360 |
| vi) | Corporate tax | 10 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + Net change in stocks
Value of Output = ii + iv = 800 + (- 40) = ₹ 760
Gross Value added at MP (GVA at MP) = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
GVA at MP = 760 – ₹360 = ₹ 400 Lakh
9. From the following data, calculate value added by firm X and by firm Y:-
| S.N | Items | (₹ lakh) |
| i) | Closing stock of firm X | 20 |
| ii) | Closing stock of firm Y | 15 |
| iii) | Opening stock of firm Y | 10 |
| iv) | Opening stock of firm X | 5 |
| v) | Sales by firm X | 300 |
| vi) | Purchases by firm X from firm Y | 100 |
| vii) | Purchases by firm Y from firm X | 80 |
| viii) | Sales by firm Y | 250 |
| ix) | Import of raw material by firm X | 50 |
| x) | Exports by firm Y | 30 |
Solution:-
Calculation of Value Added by firm X
Value of Output by Firm X = Sales by Firm X + Change in Stock of Firm X
Value of Output by Firm X = v – (i – iv) = 300 + (20 – 5) = ₹ 315
Value added by Firm X (GVA at MP by Firm X) = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption (Purchases by firm X from firm Y + Import of raw material by firm X)
Value added by Firm X = 315 – (100 + 50) = ₹ 165 lakh
Calculation of Value Added by firm Y
Value of Output by Firm Y = Sales by Firm Y + Change in Stocks of Firm Y
Value of Output by Firm Y = viii + ( ii – iii ) = 250 + ( 15 – 10 ) = ₹ 255
Value added by firm Firm Y (GVA at MP by Firm Y) = Value of Output – Intermediate consumption (purchases by firm Y from firm X)
Value added by Firm Y = 255 – 80 = ₹ 175 lakh
Note:-
Item (x) is already included in item (viii) and so it is not considered.
10. Calculate Value Added by Firms A and B from the following data:-
| S.N | Items | (₹ lakh) |
| i) | Purchases by Firm B from Firm A | 40 |
| ii) | Sales by Firm B | 80 |
| iii) | Imports by Firm B | 10 |
| iv) | Rent paid by Firm B | 5 |
| v) | Opening stock of Firm B | 15 |
| vi) | Closing Stock of Firm B | 20 |
| vii) | Purchases by Firm A from Firm B | 20 |
| viii) | Closing Stock of Firm A | 20 |
| ix) | Opening Stock of Firm A | 10 |
Solution:-
Calculation of Value Added by Firm A
Value of Output by Firm A = Sales + Change in Stock (Closing Stock – Opening Stock)
Value of Output by Firm A = i + ( viii – ix ) = 40 + (20 – 10) = ₹ 50
Value Added by Firm A = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption (Purchases by Firm A from Firm B)
Value Added by Firm A = 50 – 20 = ₹ 30
Calculation of Value Added by Firm B
Value of Output by Firm B = Sales + Change in Stock (Closing Stock – Opening Stock)
Value of Output by Firm B = ii + (vi – v) = 80 + (20 – 15) = ₹ 85
Value Added by Firm B = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption (Purchases by firm B from firm A + Imports by firm B)
Value Added by Firm B = 85 – ( 40 + 10 ) = ₹ 35 lakh
Read Here:- 50 Important Numerical of Income Method of National Income class 12
Read Here:- 50 Important Numerical of Expenditure Method of National Income Class 12
11. Calculate net value added at factor cost:-
| S.N | Items | (₹ Crore) |
| i) | Subsidies | 5 |
| ii) | Sales | 500 |
| iii) | Intermediate Consumption | 200 |
| iv) | Closing Stock | 40 |
| v) | Consumption of fixed capital | 60 |
| vi) | Indirect tax | 30 |
| vii) | Opening Stock | 50 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + Change in Stock (Closing Stock – Opening)
Value of Output = ii + ( iv – vii) = 500 + (40 – 50) = ₹ 490
Gross Value Added at Market Price (GVA at MP) = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
GVA at MP = 490 – 200 = ₹ 290
Net Value Added at Factor Cost (NVA at FC) = GVA at MP – Consumption of fixed capital – Net Indirect tax (Indirect tax – Subsidy)
NVA at FC = 290 – 60 – ( 30 – 5) = ₹ 205 crore
12. From the following information about firm X, calculate gross value added by it.
| S.N | Items | (₹ lakh) |
| i) | Domestic Sales | 300 |
| ii) | Exports | 100 |
| iii) | Production for Self Consumption | 50 |
| iv) | Purchases from firm A | 110 |
| v) | Purchases from firm B | 70 |
| vi) | Imports of raw materials | 30 |
| vii) | Change in Stock | 60 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales (Domestic Sales + Production for Self Consumption + Exports) + Change in stock (Closing Stock – Opening Stock)
Value of Output = (i + ii + iii) + vii = (300 + 100 + 50) + 60 = ₹ 510
Gross Value added by Firm X (GVA at MP) = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption (Purchases from firm A + Purchases from Firm B + Imports of Raw materials)
Gross Value Added by firm X 510 – (110 + 70 + 30) = ₹ 300 lakh
13. From the following data, find out value added by firm X:
| S.N | Items | (₹ lakh) |
| i) | Sales by Firm Y to Firm X | 400 |
| ii) | Sales by Firm X to households | 500 |
| iii) | Purchases by firm Z from Firm X | 300 |
| iv) | Opening stock of firm X | 25 |
| v) | Closing stock of firm X | 75 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales (Sales by Firm X to households + Purchases by firm Z from firm X) + Change in stock (Closing Stock by firm X – Opening stock of Firm X)
Value of Output = ( ii + iii) + ( v – iv) = ( 500 + 300 ) + ( 75 – 25 ) = ₹ 850
Value added by Firm X = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption (sales by Firm Y to firm X)
Value added by Firm X = 850 – 400 = ₹ 450 lakh
14. Calculate (a) Value of output and (b) Net Value added at factor cost from the following data:
| S.N | Items | (₹ lakh) |
| i) | Goods and services tax | 100 |
| ii) | Sales | 1000 |
| iii) | Operating Surplus | 60 |
| iv) | Opening Stock | 200 |
| v) | Consumption of fixed capital | 50 |
| vi) | Closing Stock | 200 |
| vii) | Intermediate cost | 600 |
| viii) | Subsidies | 40 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + Change in stock (Closing Stock – Opening Stock)
Value of Output = ii + (vi – iv) = 1000 + (200 – 200) = ₹ 1000
Gross Value added at Market Price (GVA at MP) = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption (intermediate cost)
GVA at MP = 1000 – 600 = ₹ 400
Net Value added at factor cost = GVA at MP – depreciation (consumption of fixed capital) – Indirect tax (Goods and service tax – subsidies)
NVA at FC = 400 – 50 – (100 – 40) = ₹ 290 lakh
14. From the data of a firm given alongside, find out net value added at factor cost:
| S.N | Items | |
| i) | Total Sales | 75000 |
| ii) | Purchase of raw materials and other inputs | 30000 |
| iii) | Indirect tax | 7500 |
| iv) | Consumption of fixed capital | 2500 |
Value of Output = Sales + Change in stock
Value of Output = 75000 + 0 = ₹ 75000
Gross value added at Market Price = Value of Output – Intermediate consumption ( Purchase of raw materials and other inputs)
GVA at MP = 75000 – 30000 = 45000
Net Value Added at Factor Cost = GVA at MP – Depreciation (consumption of fixed capital) – Net indirect tax (Indirect tax – subsidy)
NVA at MP = 45000 – 2500 – (7500 – 0)
NVA at MP = ₹ 35000
15. Given the following data, find the Net Value Added at Factor Cost by Farmer producing wheat.
| S.N | Items | (₹ in crore) |
| i) | Sale of wheat by the farmer in the local market | 6,80,000 |
| ii) | Purchase of a tracter | 5,00,000 |
| iii) | Procurement of wheat by the government from the farmer | 20,000 |
| iv) | Consumption of wheat by the farming family during the year | 5,000 |
| v) | Subsidy | 2,000 |
| vi) | Expenditure on the maintenance of existing capital stock | 10,000 |
Solution:-
Sales = i + iii + iv = 680000 + 20000 + 5000 = ₹ 705000
Value of Output = Sales + Change in Stock
Value of output = 705000 + 0 = 70500
Gross value added at MP = Value of output – Intermediate consumption (Expenditure on the maintenance of existing capital stock)
GVA at MP = 705000 – 10000 = ₹ 695000
Net value added at factor cost = GVA at MP – consumption of fixed capital – Net indirect tax (indirect tax – subsidy)
NVA at FC = 695000 – (0 + 2000) = ₹ 697000
16. Calculate Net Value Added at Factor Cost from the following data:-
| S.N | Items | (₹ in crore) |
| i) | Purchase of Machinery to be used in the production unit | 100 |
| ii) | Sales | 200 |
| iii) | Intermediate Costs | 90 |
| iv) | Indirect taxes | 12 |
| v) | Change in stock | 10 |
| vi) | Excise Duty | 6 |
| vii) | Stock of Raw Material | 5 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + Change in stock
Value of Output = ii + v = 200 + 10 = ₹ 210
Gross Value added at Market Price = Value of Output – Intermediate Costs
GVA at MP = 210 – 90 = 120
Net Value added at Factor cost = GVA at MP – Depreciation – Net Indirect tax (Indirect tax – subsidy)
NVA at FC = 120 – 0 – (12 – 0) = ₹ 108 crore
17. From the following data relating to a firm, calculate its Net Value Added at Factor Cost:
| S.N | Items | (₹ in lakh) |
| i) | Subsidy | 40 |
| ii) | Sales | 800 |
| iii) | Depreciation | 30 |
| iv) | Exports | 100 |
| v) | Closing Stock | 20 |
| vi) | Opening Stock | 50 |
| vii) | Intermediate purchases | 500 |
| viii) | Purchase of Machinery for own use | 200 |
| ix) | Import of raw material | 60 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + Change in stock (closing stock – opening stock)
Value of Output = 800 + (20 – 50) = 770
Gross value added at Factor cost = Value of Output – intermediate consumption
GVA at MP = 770 – 500 = 270
Net Value added at Factor cost = GVA at MP – Depreciation – Net Indirect tax (Indirect tax – subsidy)
NVA at Fc = 270 – 30 – ( 0 – 40) = ₹ 280 lakh
Notes:- Exports are not considered as it is already included in Sales.
18. Calculate Gross Domestic Product at Market Price by Production Method.
| S.N | Items | ₹ crore |
| i) | Intermediate consumption of: a) Primary sector b) Secondary Sector c) Tertiary Sector | 500 400 300 |
| ii) | Value of Output a) Primary Sector b) Secondary Sector c) Tertiary Sector | 1000 900 700 |
| ii) | Rent | 10 |
| ix) | Emoluments of Employees | 400 |
| v) | Mixed Income | 650 |
| vi) | Operating Surplus | 300 |
| vii) | Net Factor Income from abroad | – 20 |
| viii) | Interest | 5 |
| ix) | Consumption of fixed capital | 40 |
| x) | Net Indirect tax | 10 |
Solution:-
GDP at MP = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
GDP at MP = ( iia + iib + iic ) – ( ia + ib + ic )
GDP at MP = ( 1000 + 900 + 700 ) – ( 500 + 400 + 300 )
GDP at MP = 2600 – 1200
GDP at MP = 1400 crore
19. Calculate Gross Domestic Product at market price from the following data:-
| S.N | Items | (₹ lakh) |
| i) | Net Value added at market price by: a) Primary Sector b) Secondary Sector c) Tertiary Sector | 700 1000 1000 |
| ii) | Net Exports | – 10 |
| iii) | Net Indirect tax | 100 |
| iv) | Value of Intermediate consumption in: a) Primary Sector b) Secondary Sector c) Tertiary Sector | 200 300 300 |
| v) | Consumption of fixed capital in: a) Primary Sector b) Secondary Sector c) Tertiary Sector | 20 50 30 |
GDP at MP = Net Value at added at MP + Depreciation
GDP at MP = (ia + ib + ic) + (va + vb + vc)
GDP at MP = (700 + 1000 + 1000) + (20 + 50 + 30)
GDP at MP = 2700 + 100
GDP at MP = 2800 lakh
20. Calculate Net Value Added at factor cost from the following data:0
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Purchase of machinery to be used in the production unit. | 100 |
| 2. Sales | 200 |
| 3. Intermediate costs | 90 |
| 4. Indirect taxes | 12 |
| 5. Changes in Stock | 10 |
| 6. Excise duty | 6 |
| 7. Stock of Raw Material | 5 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Sales + change in stock
Value of Output = 200 + 10 = 210
GDP at MP = Value of Output – Intermediate consumption
GDP at MP = 210 – 90
GDP at MP = 120
Net Value added at factor cost (NDP at FC) = GDP at MP – consumption of fixed capital – Net Indirect tax (Indirect tax – subsidy)
NVA at FC = 120 – 0 – ( 12 – 0 )
NVA at FC = ₹ 108 crore
21. Find NVA at FC from the following.
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Sales | 800 |
| 2. Taxes on production | 50 |
| 3. Depreciation | 70 |
| 4. Opening Stock | 100 |
| 5. Closing Stock | 80 |
| 6. Intermediate cost | 200 |
Solution:-
Value of output = Sales + Closing stock – Opening stock
Value of Output = 800 + 80 – 100
Value of Output = 780
GDP at MP = Value of output – Intermediate cost
GDP at MP = 780 – 200
GDP at MP = ₹ 580
NVA at FC = GDP at MP – Depreciation – Taxes on production
NVA at FC = 580 – 70 – 50
NVA at FC = ₹ 460 lakh
22. Calculate GVA at MP from the following:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Purchase by Firm A from Firm B | 100 |
| 2. Purchase by Firm B from Firm A | 150 |
| 3. Sales by Firm A | 200 |
| 4. Sales by Firm B | 300 |
| 5. Exports by Firm B | 30 |
| 6. Change in stock of Firm A | – 20 |
| 7. Change in stock of Firm B | 10 |
Solution:-
GVA at MP by A = Sales by Firm A + Change in stock of Firm A – Purchase by firm a From Firm B
GVA at MP by A = 200 – 20 – 100
GVA at MP by A = ₹ 80 crore
GVA at MP by B = Sales by Firm B + Change in sock of Firm B – Purchase by Firm B from Firm A
GVA at MP by B = 300 + 10 – 150
GVA at MP by B = ₹ 160 crore
Note:- item 5th was not considered as it is already included in sales of B. Purchase from one firm by another firm is considered as intermediate consumption.
23. Calculate national income from the following data. Assume that there are only two properties, firm A and Firm B in the economy:
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Purchases of materials, etc. by Firm A from Firm B | 20 |
| 2. Purchases of materials, etc. by Firm B from Firm A | 30 |
| 3. Value of output produced by Firm A | 100 |
| 4. Value of output produced by Firm B | 80 |
| 5. Payment of indirect tax by Firm A | 10 |
| 6. Payment of indirect tax by Firm B | 5 |
| 7. Consumption of fixed capital by Firm B | 5 |
| 8. Consumption of fixed capital by Firm A | 10 |
| 9. net change in stocks of Firm A | – 7 |
| 10. Net change in stock of Firm B | 7 |
| 11. Net factor income from abroad | – 5 |
Solution:-
Value added by Firm A (GDP at MP) = Value of output Produced by Firm A – Purchases of material, etc by firm A from firm B
Value added by Firm A = 100 – 20 = 80
Value added by Firm B = Value of output produced by Firm B – Purchases of material, etc. by firm B from Firm A
Value added by Firm B = 80 – 30 = 50
GDP at MP = Value added by Firm A + Value added by Firm B
GDP at MP = 80 + 50 = ₹ 130
NNP at FC = GDP at MP – Consumption of fixed capital by firm A – consumption of fixed capital by firm B + net factor income from abroad – payment of indirect tax by firm A – payment of indirect by Firm B
NNP at FC = 130 – 10 – 5 – 5 – 10 – 5
NNP at FC = ₹ 95 crore
24. Calculate GDP at MP and NDP at FC from the following data. Assume that there are only two sectors A and B in the economy.
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Closing stock of sector A | 20 |
| 2. Opening stock of sector B | 5 |
| 3. Opening stock of sector A | 30 |
| 4. Closing stock of sector B | 15 |
| 5. Sales by sector B | 200 |
| 6. Sales by sector A | 150 |
| 7. Goods and Services tax paid by section A | 15 |
| 8. Consumption of fixed capital by sector B | 10 |
| 9. Consumption of fixed capital by sector A | 10 |
| 10. Subsidies to sector B | 5 |
| 11. Intermediate consumption by sector A | 70 |
| 12. Intermediate consumption by sector B | 60 |
| 13. Net factor income from abroad | 10 |
Solution:-
Value added by sector A = Sales by sector A + Closing stock of sector A – Opening stock of sector A – Intermediate consumption by sector A
Value added by sector A = 150 + 20 – 30 – 70
Value added by sector A = 70
Value added by sector B = Sales by sector B + Closing stock of sector B – Opening stock of Sector B – Intermediate consumption by sector A
Value added by sector B = 200 + 15 – 5 – 60
value added by sector B = 150
GDP at MP = Value added by sector A + Value added by sector B
GDP at MP = 70 + 150
GDP at MP = 220
NDP at FC = GDP at MP – consumption of fixed capital by sector A – consumption of fixed capital by sector B – Goods and services tax paid by sector A + subsidies to sector B
NDP at FC = 220 – 10 – 10 – 15 + 5
NDP at FC = ₹ 190 crore
25. From the following data, calculate “gross value added at factor cost.”
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Sales | 180 |
| 2. Rent | 5 |
| 3. Subsidies | 10 |
| 4. Change in stock | 15 |
| 5. Purchase of raw materials | 100 |
| 6. Profits | 25 |
Solution:-
value of output = Sales + change in stock
Value of Output = 180 + 15
Value of Output = 195
Gross Value added at MP (GDP at MP) = Value of Output – purchase of raw materials
GDP at MP = 195 – 100
GDP at MP = 95
Gross value added at factor cost = GDP at MP – indirect tax + subsidies
Gross value added at factor cost = 95 – 0 + 10
Gross Value added at factor cost ₹ 105
26. From the following data, calculate “gross value added at factor cost.”
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Net indirect tax | 20 |
| 2. Purchase of intermediate products | 120 |
| 3. Purchase of machines | 3oo |
| 4. Sales | 250 |
| 5. Consumption of fixed capital | 20 |
| 6. Change in stock | 30 |
Solution:-
Value of output = Sales + Change in stock
Value of output = 250 + 30
Value of output = 280
gross value added at MP (GDP at MP) = Value of output – purchase of intermediate products
gross value added at MP = 280 – 120
gross value added at MP = 160
gross value added at FC = gross value added at FC – Net indirect tax
gross value added at FC = 160 – 20
gross value added at FC = ₹ 140 crore
27. Calculate Net Value added at Market Price from the following data:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Depreciation | 5 |
| 2. Sales | 100 |
| 3. Opening stock | 20 |
| 4. Intermediate consumption | 70 |
| 5. Excise Duty | 10 |
| 6. Change in stock | – 10 |
Solution
Value of Output = Sales + change in stock
Value of Output = 100 – 10 = 90
GDP at MP = Value of Output – Intermediate consumption
GDP at MP = 90 – 70
GDP at MP = 20
Net value added at MP = GDP at MP – Depreciation
Net Value added at MP = 20 – 5
Net Value added at MP = ₹ 15 crore
28. Calculate Gross Value Added at Factor Cost:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Units of output sold (units) | 1000 |
| 2. Price per unit of output | 30 |
| 3. Depreciation | 1000 |
| 4. Intermediate cost | 12000 |
| 5. Closing stock | 3000 |
| 6. Opening stock | 2000 |
| 7. Excise | 2500 |
| 8. Sales Tax | 3500 |
Solution:-
Value of Output = Units of output sold * Price per unit of output + Closing stock – Opening stock
Value of Output = 1000 * 30 + 3000 – 2000
Value of Output = 30000 + 1000
Value of Output = 31000
GDP at MP = Value of output – intermediate cost
GDP at MP = 31000 – 12000
GDP at MP = 19000
Gross value added at Factor Cost = GDP at MP – Excise – sales tax
Gross value added at Factor Cost = 19000 – 2500 – 3500
Gross Value added at Factor Cost = ₹ 13000
Further Reading
| S.N | Topics |
| 1. | What is GDP Deflator |
| 2. | What are externalities in economics |
| 3. | Limitations of GDP as a measure of welfare |
| S.N | Topics |
| 1. | 150+ Numerical of Value Added Method |
| 2. | 150+ Numerical of Income Method |
| 3. | 150+ Numerical of Expenditure Method |
| 4. | 150+ Numerical of National Income and related aggregates |
| S.N | Topics |
| 1. | 250+ MCQs of National Income |




Best questions which opened the mind.
Are you from 2021-22 batch??
Please give some hard question
Provide very hard questions calculation of two aggregate with other things like mixed income interest change in stock