
Nominal GDP and Real GDP class 12 CBSE Board
Nominal GDP and Real GDP are the important topics of the national income chapter of Macroeconomics class 12 CBSE Board.
It is a short topic and in this lecture, we will discuss it in detail covering its all aspects.
The concept of real and nominal GDP arises with the question of whether the calculation of GDP indicates the actual welfare of the society or not.
What is Nominal GDP?
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is the money value of all goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country in a year.
But when money value is calculated at the current prices of an accounting year it is called Nominal GDP.
Nominal GDP with an example
Let’s suppose in 2021 there are 200 quantities of goods produced and the current price in the market is ₹ 50.
Thus the Nominal GDP of 2021 is
Nominal GDP = quantity produced * current year market price
Nominal GDP = 200 * 50 = ₹ 10,000
If the price in 2022 changes to ₹ 60
The Nominal GDP of 2022 would be
Nominal GDP (2022) = 200 * 60 = ₹ ₹ 12000
Thus Nominal GDP also refers to GDP at current prices.
Note:- Nominal GDP either quantity of goods changes or current year prices changes.
Definition of Nominal GDP
Different textbooks have given the definition of Nominal GDP. Let’s see how they differ. You can learn anyone out of them that looks easy to you.
It is the Market value of the final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country during an accounting year, as estimated using the current year prices.
T.R Jain
It is the money value of final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in a year, measured at the prices of the current year.
Sandeep Garg
When the value of the final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country expressed in terms of current market value. It is called Nominal GDP.
S.K Aggarwal
Other Names of Nominal GDP
- GDP at current prices.
- Nominal National Income
Formula of Nominal GDP
Nominal GDP = quantity of final goods and services produced during an accounting year * Prices prevailing during the accounting year.
Nominal GDP = Q * P
Example of Nominal GDP
Let’s assume in India during 2020-21 10 chairs, 20 grocery products, and 30 Machinery are produced. The current market prices of groceries are chair ₹50 per piece, grocery ₹100 per piece, machinery ₹70 per piece.
Hence
Nominal GDP = 10 * 50 + 20 * 100 + 30 * 70 = ₹500 + ₹2000 + ₹2100 = ₹4600
What is Real GDP?
When GDP is calculated eliminating the effect of inflation it is called Real GDP. It is calculated at the price of the Base year.
It is the market value of the final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country during an accounting year, as estimated using the base year prices.
T.R Jain
It is the money value of final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in a year, measured at base year price.
Sandeep Garg
Other names of Real GDP
- GDP at constant prices.
- Real National Income
- Real Domestic Income
Formula of Real GDP
In order to calculate Real GDP, a base year is decided that is free from price fluctuation. So far India’s base year is 2011-12. But the government would change it to 2017-18. Many economists advising 2020-21 as the base year.
Example of Real GDP
For example, there are 100 units of goods and services are produced in 2020-21. Price prevailing in the same year are Rs. 10 per unit. But the price in 2011-12 was Rs 8 per unit.
Hence Real GDP would be 100 * 8 = ₹800
Difference between Nominal GDP and Real GDP
| Basis | Nominal GDP | Real GDP |
| Meaning | It refers to the money value of final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in a year, measured at the current price | It is the money value of final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in a year, measured at base year price. |
| Indicates Economic growth | it is not a good indicator of economic growth | It better indicates economic growth. |
| Causes of change | It changes when both price and quantity change or anyone. | It only changes when only quantity changes. |
| Comparison | It is not a good tool to compare the domestic income of the different years. | It is a good tool. |
| Calculation | Quantity * current price | Quantity * Base year price |
| Alternative Name | Domestic income at the current price | Domestic income at constant price. |
Note:- If the difference between nominal and real national income is asked change domestic to national.
What is GDP deflator?
Define GDP deflator
It refers to the ratio between GDP at current prices and GDP at constant prices. It is expressed as under:
Formula of GDP deflator
GDP Deflator = GDP at current prices/GDP at Constant prices * 100
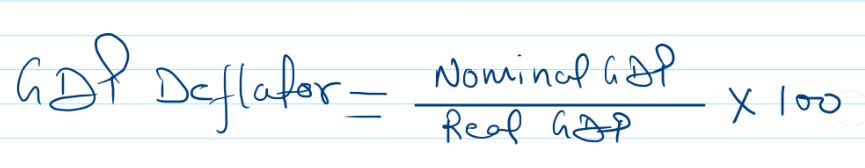
This formula can also be written as
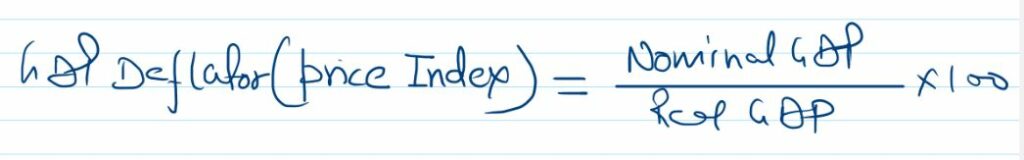
With help of the GDP deflator formula. We can easily convert Nominal GDP into Real GDP, provided the price index (base year price) is given.
Further Reading:-
| S.N | Topics |
| 1. | What is GDP Deflator |
| 2. | What are externalities in economics |
| 3. | Limitations of GDP as a measure of welfare |
| S.N | Topics |
| 1. | 150+ Numerical of Value Added Method |
| 2. | 150+ Numerical of Income Method |
| 3. | 150+ Numerical of Expenditure Method |
| 4. | 150+ Numerical of National Income and related aggregates |
| S.N | Topics |
| 1. | 250+ MCQs of National Income |



